Cost Methodology
If the facility has a cost accounting system, actual costs are submitted by the facility. If the facility does not have a cost accounting system, a departmental level ratio of cost to charges (RCC) cost is calculated using factors from the annual Medicare cost report.
Calculating RCC Costs
The process is as follows:
- A ratio of cost to charges (RCC) is calculated for each facility department.
- These ratios are then used to estimate cost for each department for each patient.
- The calculated costs for each patient are then summed to derive Total Cost for each patient.
- The RCC is recalculated with each data submittal.
An Example of Calculating RCC Costs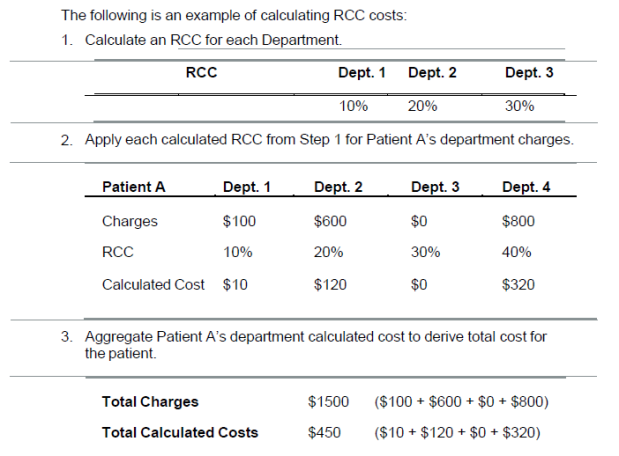
Cost Methodology for Risk-Adjusted Analyses
For CareScience analyses, Expected Cost is derived using procedural cost method.
For 3M™ analyses, Expected Cost is derived using procedural cost method. Observed Cost is always based on the cost method submitted to Premier.
Cost Definitions in the Perspective Database
The Perspective Database has two cost definitions: variable and fixed.
- Variable costs are expenses that relate directly to or vary with the activity (volume) of the department.
- Fixed costs are expenses that do not relate directly to or vary with the activity (volume) of the department.
The following are examples of variable and fixed cost expenses:
|
Variable Costs |
Fixed Costs |
|---|---|
|
Hands-on patient care |
Overhead departments |
|
Films |
Management/supervision |
|
Drugs |
Repair and maintenance |
|
Medical Supplies |
Non-billable professional fees |
|
Billable professional fees |
Office supplies |
|
X-ray technician |
Transcription Transport Sterilization techs Education Contract expense Depreciation |