Operators
Refer to the following for information for using operators in prompts.
OR Operator
The OR operator is used to run a query that will return items from either list.
In the following scenarios, the total number of cases is 3,665 for the population. These examples show how using operators within prompts change the number of cases in the population.
Example 1
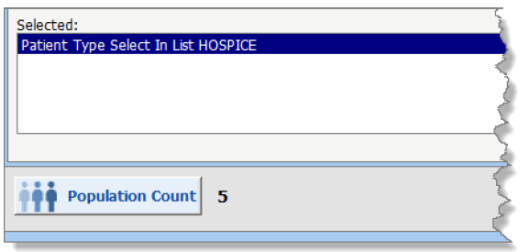
In this example, you have filtered the population by all patients who had a patient type of Hospice OR had a diagnosis of Acute Sinusitis.
There are five patients in Hospice:
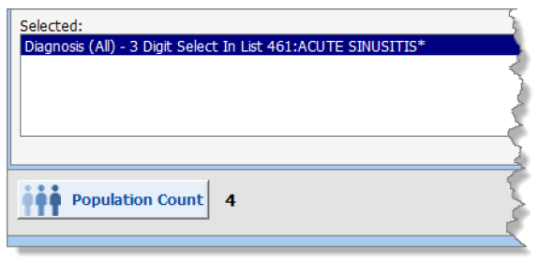
and four with a diagnosis of Acute Sinusitis:
Each population has a unique set of patient IDs, which means that none of the patients had both a patient type of Hospice and a diagnosis of Acute Sinusitis:
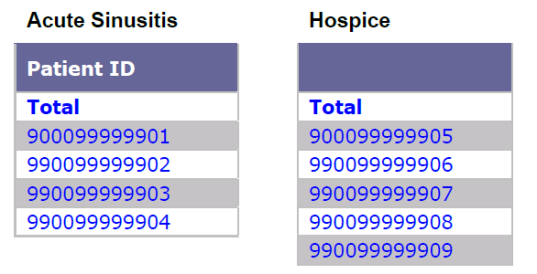
Therefore, the population that returns for either patient type Hospice OR diagnosis Acute Sinusitis includes nine patients:
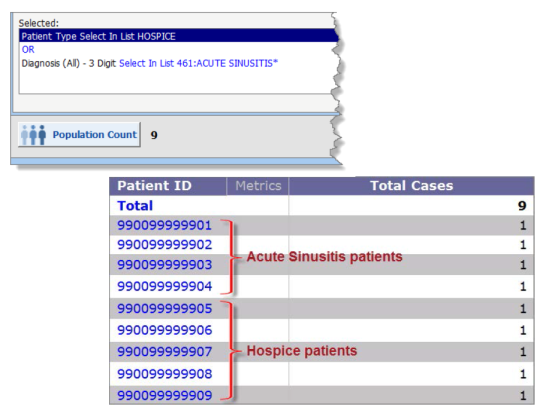
Note: If, for example, Patient 990099999909 had both a patient type of Hospice and a diagnosis of Acute Sinusitis, then the population count would be 8, because this patient would meet both criteria and only be counted once.
Example 2
In this example, you run the same query from Example 1, but filter the population by all patients who did not have a patient type of Hospice OR did not have a diagnosis of Acute Sinusitis.
Total population before the population is filtered:
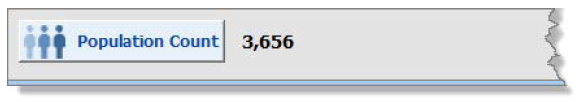
There are no exclusions from the population, so after filtering, the population count does not change:
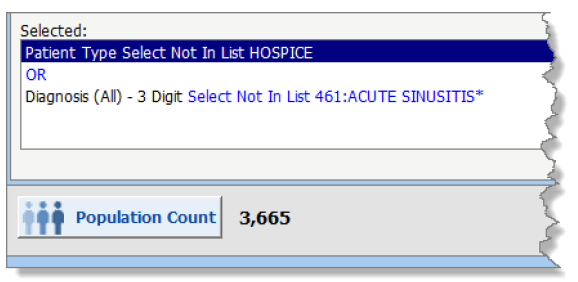
- There are 3,665 total patients.
- There are 4 patients with a patient type of Hospice and 5 patients with a diagnosis of Acute Sinusitis.
- There is no overlap of patients that meet either of these criteria. There is no patient in Hospice who also has Acute Sinusitis and there is no patient who has Acute Sinusitis who is in Hospice.
- Therefore, the patients who are not in Hospice are included in the population of patients with a diagnosis of Acute Sinusitis. Similarly, the patients who do not have a diagnosis of Acute Sinusitis are included in the population of Hospice patients. The union, or the total number of unique or distinct patients in the set, will be the total population, because there is no overlap.
AND Operator
The AND Operator is used to run a query will return items that are in both lists.
Example 1
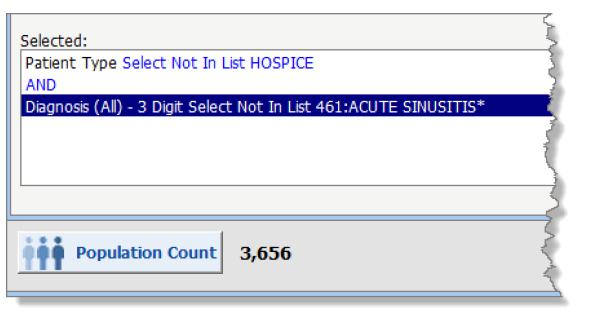
You filter the population by all patients who had a patient type of Hospice AND had a diagnosis of Acute Sinusitis.
There are no patients who meet both criteria, so the population count is 0. None of the patients have the diagnosis of Acute Sinusitis and a patient type of Hospice:
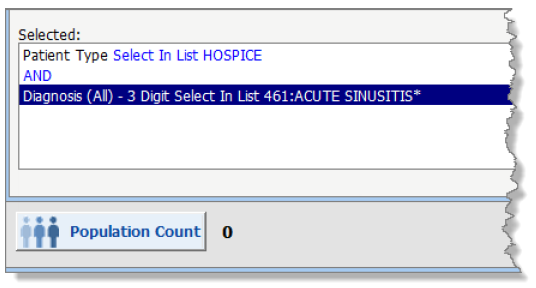
There are 5 patients with a patient type of Hospice and 4 patients with a diagnosis of Acute Sinusitis. So if the user wants a population to return for all patients who are not in Hospice AND do not have a diagnosis of Acute Sinusitis, then the population must only include patients who meet both of these criteria, or exclude patients who are Hospice and have Acute Sinusitis.
- Total number of patients in the population: 3,665.
- Total number of patients who are Hospice (5).
- Total number of patients who have Acute Sinusitis (4).
- Total number of patients in the population, excluding Hospice and Acute Sinusitis patients is 3,665 – 9 = 3,656.